A new publication titled “Machine Learning Enabled Orthogonal Camera Goniometry for Accurate and Robust Contact Angle Measurements” was published in Scientific Reports, in January 2023.
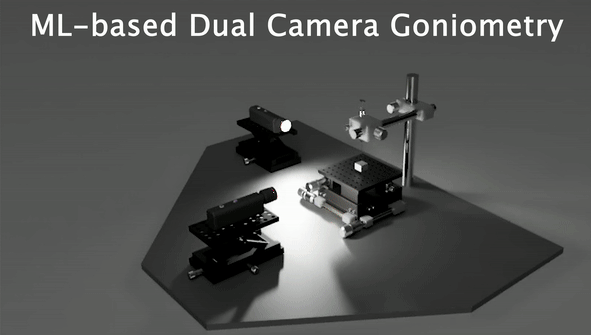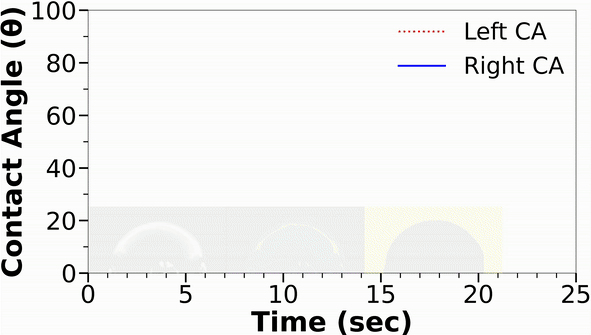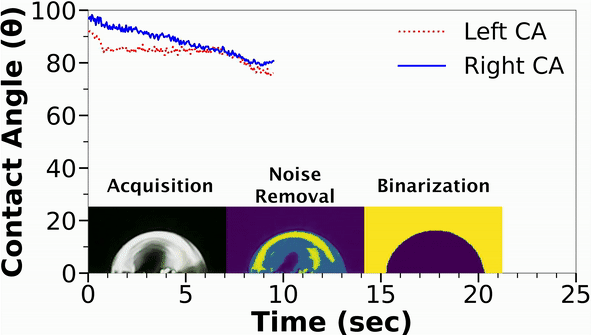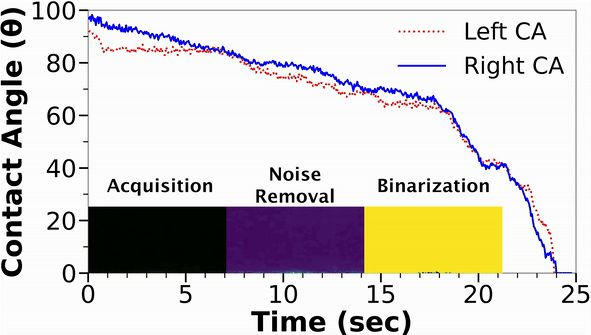
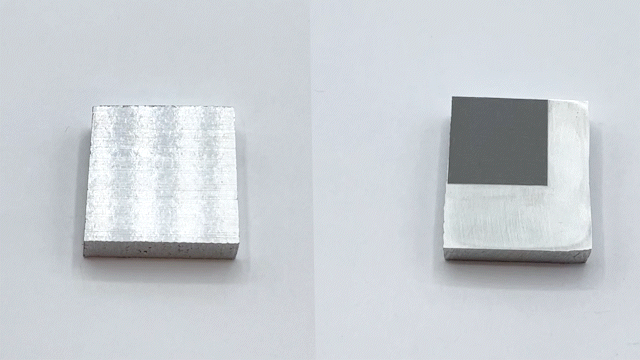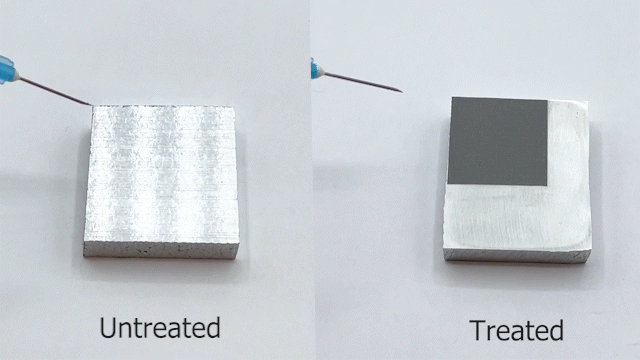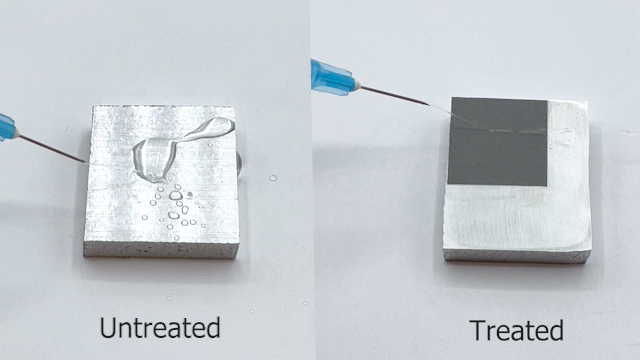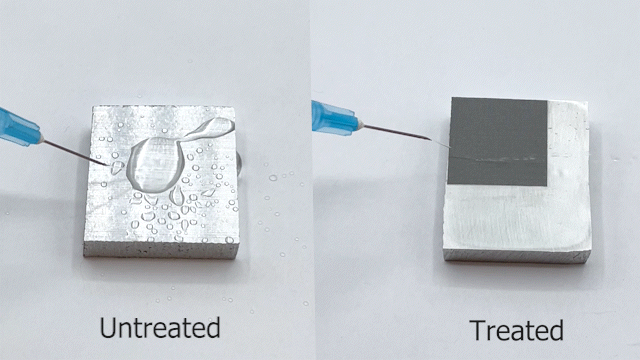
Understanding the wetting properties of surfaces is crucial for physical, chemical, and biological processes. However, conventional methods for accurately estimating contact angles, especially on hydrophilic surfaces, can be limited by optical distortions caused by moving droplets. In response, we have developed a new setup that combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) with an automated orthogonal camera goniometer to estimate contact angles with high precision.
Our algorithm was trained on a dataset of 3375 images, including different lighting conditions and various degrees of Gaussian blurring, and was found to be less sensitive to edge effects than existing goniometers. In addition, our method was able to accurately analyze droplets of different colors and chemistries on a range of surfaces. The resulting contact angle measurements from our automated orthogonal camera goniometer exhibited significantly lower average standard deviation (6.7°) and coefficient of variation (14.9%) compared to existing techniques (average standard deviation of 14.6° and coefficient of variation of 29.2%). This demonstrates the reliability and precision of our method for characterizing the wetting properties of non-spherical droplets on heterogeneous surfaces.
This is the first article from our group’s Ph.D. candidate Hossein Kabir. Congratulations Hossein!
The article can be accessed here.